How Is the Electronegativity Trend Related to the First Ionization
Existence of these trends is due to the similarity in atomic structure of the elements in their group. The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity.

Periodic Table Trends Chart Vector Illustration Scheme Stock Vector Illustration Of Graphic Che Study Biology Chemistry Lessons Amazing Science Experiments
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract the electrons when the atom is part of a compound.

. What are 1st 2nd and 3rd ionization energies. Trend-wise ionization energy tends to increase while one progresses across a period because the greater number. Here is a look at the periodic table trends of electronegativity atomic radius electron affinity metallic character and ionization energy.
This is because the electrons are being held in closer to the protons which have opposing charges and therefore hold on to them in an atom with a small radius. Ionization energy exhibits periodicity on the periodic table. This occurs due to a greater charge on the nucleus causing the electron bonding pairs to be very attracted to atoms placed further right on the periodic table.
Electronegativity increases as you move up the table whereas ionization energy decreases. This depends on the number of protons and on the orbitals that the electron occupies. Electronegativities generally decrease from top to bottom of a group.
The general trend is for ionization energy to increase moving from left to. Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element including its size and its electronic properties. It shows how an atom can swiftly form a chemical bond.
The first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the first electron and generally the nth ionization energy is the energy required to remove the atoms nth electron after the n1 electrons before it has been removed. How is the electronegativity trend related to the first ionization energy trend. Electronegativity symbolized as χ is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons or electron density when forming a chemical bond.
Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gas phase. Although there is a general trend toward an increase in the first ionization energy as we go from left to right across this row there are two minor inversions in this pattern. Ionization always requires energy.
The first ionization energy decreases and the electronegativity decreases. These trends are readily. There is extra stability when a type of orbital is half filled or completely filled.
Actually the trend of electronegativity and first ionization energy is the same but just keep In mind there are several exceptions. The amount of energy required to separate one electron from its atom first ionization energy depends on how tightly held the electron is. Relationship between Electronegativity and Ionization Energy.
Major periodic trends include. As a result the most electronegative elements are found on the top right of the periodic table while the least electronegative elements are found. The figure below shows the first ionization energies for elements in the second row of the periodic table.
An atoms electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. Also effective nuclear charge decreases. Atoms are the building blocks of all existing substances.
For example the first ionization energy of N is actually larger than O. On the periodic table electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group. As we move from top to bottom in a periodic table atomic radius increases.
An increase in ionization energy led to an increase in the ionization energy. The key difference between electronegativity and ionization energy is that electronegativity explains the attraction of electrons while ionization energy refers to the removal of electrons from an atom. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract the electrons in a bond towards it while ionization energy is the energy a neutral atom needs to remove an electron from it.
Postby 304984981 Mon May 21 2018 302 am. Hereof what are the general trends in first ionization energy. January 10 2012 Posted by Dunee.
If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 17 the character of the bond will be ionic. If the radius is larger then those electrons on the outer edge of the atom arent being held in so close and are easier to lose - requiring a lower amount. Exceptions to the General Pattern of First Ionization Energies.
Electronegativity and first ionization energy both decrease as you move up the periodic table. The greater the electronegativity the greater the first ionization energy. Periodic trends arising from the arrangement of the.
Families or periods and because of the periodic nature of elements. Electronegativity values generally increase from left to right across the periodic table. How is the electronegativity trend related to the first ionization energy trend-.
The higher the associated electronegativity the. The highest electronegativity value is for fluorine. Electronegativity and first ionization energy both increase going up the periodic table.
Electronegativity decreases as you move up the table whereas ionization energy increases. The most common units of ionization energy are kilojoules per mole kJM or electron volts eV. If the difference in electronegativity is between 04 and 17 the character of the bond is polar covalent.
This makes the recurring element properties noticeable in this table. Fluorine is the most electronegative element. Electronegativity ionization energy electron affinity atomic radius and metallic character.
Electronegativity ionization energy electron affinity atomic radius melting point and metallic character. Electronegativity is a measure of an atoms ability to attract shared electrons to itself. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to pull electrons towards it.
Whereas ionization energy increases from left to right in a row and. The first ionization energy is the energy it takes to. The smaller the radius the higher the ionization energy.
Electronegativity increases as you move across the periodic table from left to right. Electronegativity is the attract electron while ionization energy is energy required to remove electron and hence if an atom has great electronegativity it cannot loss an electron easily.

8 4 Ionization Energy Ionization Energy Chemistry Chemistry Experiments

Periodic Table Outermost Electron Orbitals Science Notes And Projects Physical Science Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

Periodic Trends Chemwiki Electron Affinity Ionization Energy Chemistry Textbook

How To Use A Periodic Table Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Teaching Chemistry

Periodic Trends Electronegativity Ionization Energy And Atomic Radius Ionization Energy Chemistry Worksheets Classroom Tools

Periodic Trends Chemwiki Ionization Energy Chemistry Electron Affinity
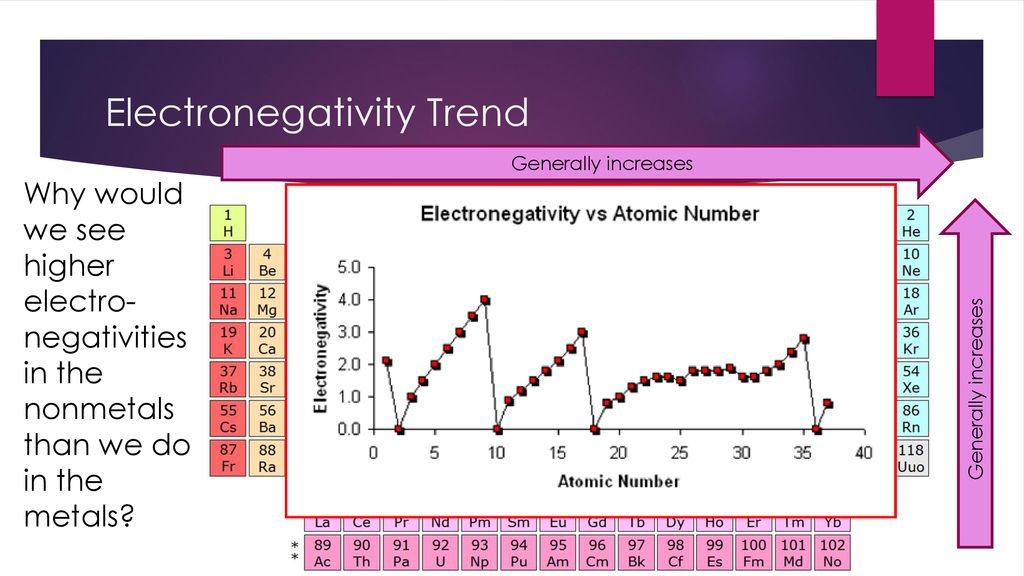
Periodic Trends Notes In Packet Ppt Download
Ionization Energy And Electronegativity

Trends In The Periodic Ta Le Ionization Energy Atomic Radius Electron Affinity Electronegativity Ionization Energy Electron Affinity Electrons

What Did You Do Today At School Electronegativity Trends 3d Periodic Table Chemistry Activities Teaching Chemistry High School Science Activities
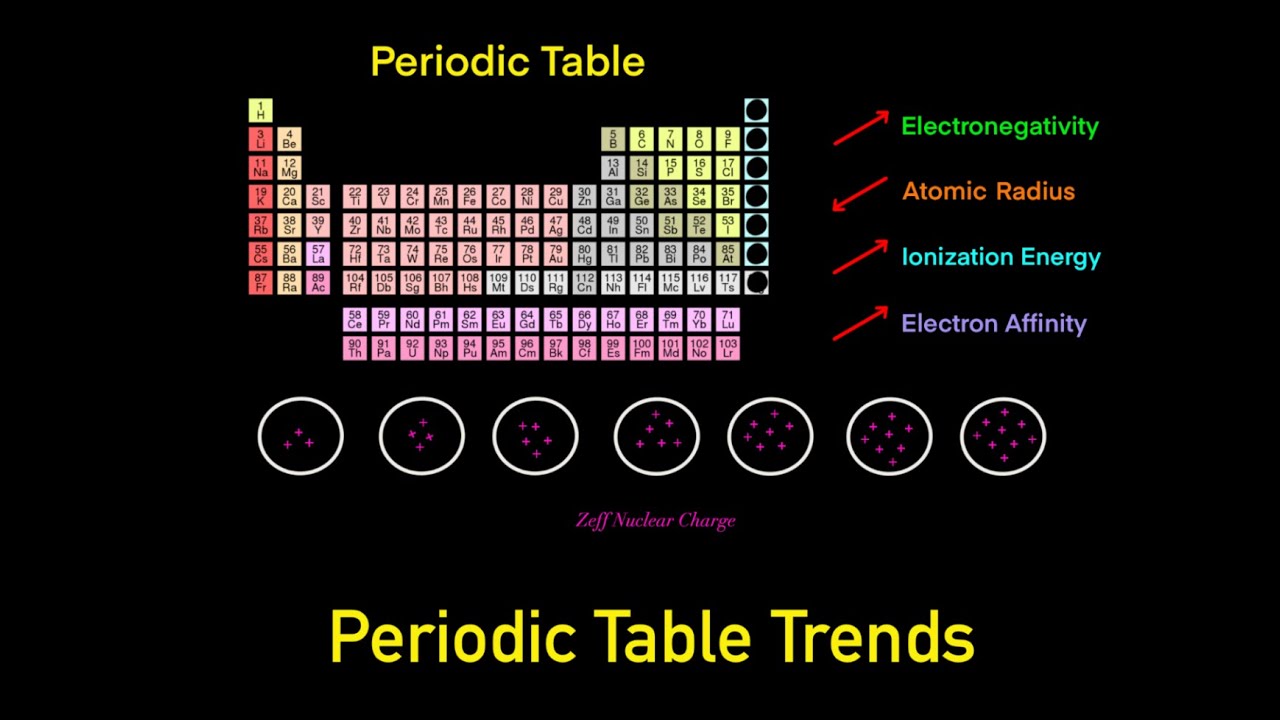
Periodic Table Trends Trick Electronegativity Atomic Radius Ionization Energy Electron Affinity Youtube

Chart Summarizes The Major Trends In The Properties For Elements In The Periodic Table Trends Electr Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

Periodic Trends Made Easy Chemtalk

Trends In The Periodic Table Chpt 7 1 Atomic Radius Size 2 Ionization Energy 3 Electronegativity The Th Ionization Energy Periodic Table Ionic Bonding
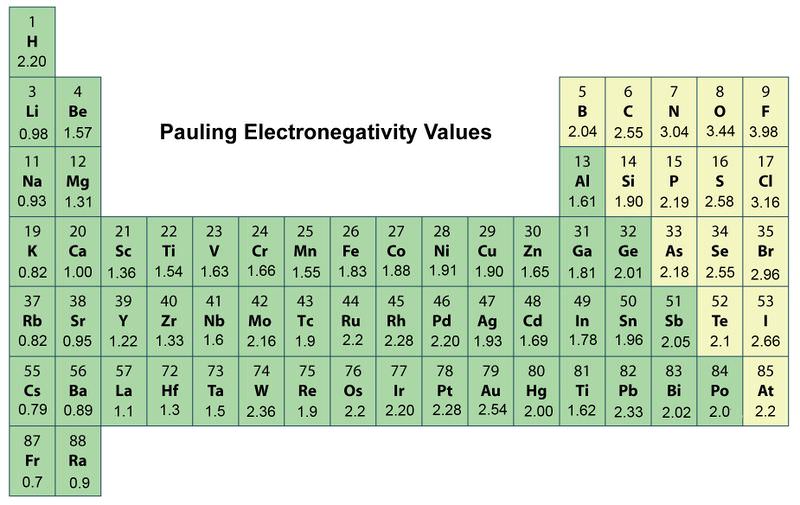
Periodic Trends In Electronegativity Ck 12 Foundation

Easy To Use Chart Of Periodic Table Trends Teaching Chemistry Science Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

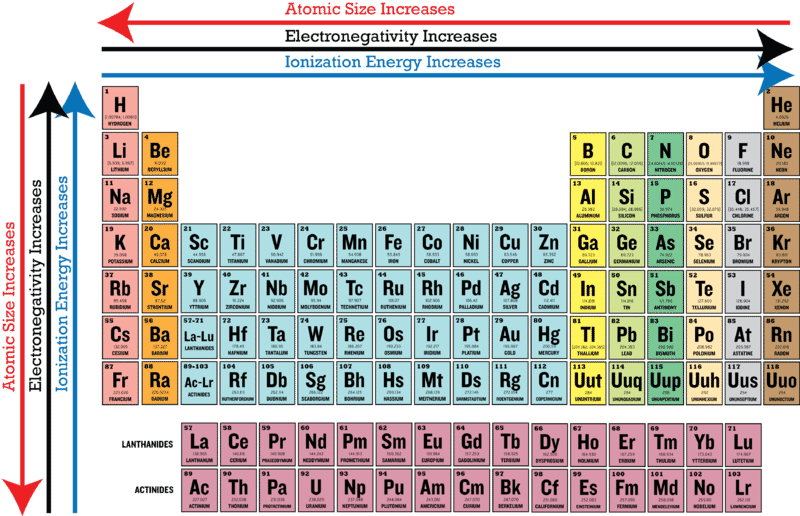
Comments
Post a Comment